How To Clean Hepa Filter Shark Xhf680
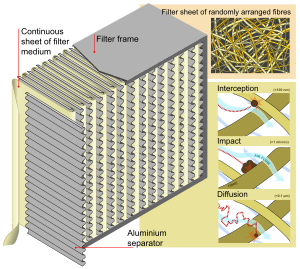
HEPA filter corrugated internal structure and aluminium back up along with the clarification of its functioning principle (interception, impact and diffusion of dust particles through a dense non-woven fiber textile)
HEPA (, high-efficiency particulate air) filter,[1] also known as loftier-efficiency particulate absorbing filter and high-efficiency particulate arrestance filter,[2] is an efficiency standard of air filter.[three]
Filters coming together the HEPA standard must satisfy certain levels of efficiency. Common standards crave that a HEPA air filter must remove—from the air that passes through—at least 99.95% (ISO, European Standard)[4] [five] or 99.97% (ASME, U.Southward. DOE)[half-dozen] [seven] of particles whose diameter is equal to 0.3 μm, with the filtration efficiency increasing for particle diameters both less than and greater than 0.3 μm.[8] HEPA filters capture pollen, dirt, dust, moisture, leaner (0.2-2.0 μm), virus (0.02-0.3 μm), and submicron liquid aerosol (0.02-0.5 μm).[9] [10] [11] Some microorganisms, for case, Aspergillus niger, Penicillium citrinum, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Bacillus subtilis are captured by HEPA filters with photocatalytic oxidation (PCO). HEPA is likewise able to capture some viruses and bacteria which are ≤0.3 μm.[12] HEPA is also able to capture floor dust which contains Bacteroidia, Clostridia, and Bacilli.[13]
HEPA was commercialized in the 1950s, and the original term became a registered trademark and later a generic trademark for highly efficient filters.[14] HEPA filters are used in applications that crave contamination control, such as the manufacturing of difficult disk drives, medical devices, semiconductors, nuclear, food and pharmaceutical products, likewise as in hospitals,[15] homes, and vehicles.
Mechanism [edit]

The four primary filter collection mechanisms: diffusion, interception, inertial impaction, and electrostatic attraction

Archetype Drove Efficiency Curve with Filter Collection Mechanisms
HEPA filters are composed of a mat of randomly arranged fibers.[sixteen] The fibers are typically composed of polypropylene or fiberglass with diameters between 0.5 and 2.0 micrometers. Most of the fourth dimension, these filters are equanimous of tangled bundles of fine fibers. These fibers create a narrow convoluted pathway through which air passes. When the largest particles are passing through this pathway, the bundles of fibers bear similar a kitchen sieve which physically blocks the particles from passing through. However, when smaller particles pass with the air, equally the air twists and turns, the smaller particles cannot keep upward with the motion of the air and thus they collide with the fibers. The smallest particles have very little inertia and they always move around the air molecules like they are bombarded by these molecules (Brownian motility). Considering of their movement, they cease up crashing into the fibers.[17] Key factors affecting its functions are fiber bore, filter thickness, and face velocity. The air space between HEPA filter fibers is typically much greater than 0.3 μm. HEPA filters in very high level for smallest particulate matter. Dissimilar sieves or membrane filters, where particles smaller than openings or pores tin pass through, HEPA filters are designed to target a range of particle sizes. These particles are trapped (they stick to a fiber) through a combination of the following three mechanisms:
Diffusion [edit]
- Particles beneath 0.3 μm are captured past diffusion in a HEPA filter. This machinery is a result of the collision with gas molecules by the smallest particles, especially those beneath 0.1 μm in diameter. The pocket-size particles are effectively blown or bounced around and collide with the filter media fibers. This behavior is like to Brownian motility and raises the probability that a particle will be stopped by either interception or impaction; this mechanism becomes dominant at lower airflow.
Interception [edit]
- Particles following a line of flow in the air stream come up within one radius of a fiber and adhere to it. Mid size particles are being captured past this process.
Impaction [edit]
- Larger particles are unable to avoid fibers by post-obit the curving contours of the air stream and are forced to embed in one of them directly; this effect increases with diminishing fiber separation and higher air flow velocity.
Diffusion predominates below the 0.one μm diameter particle size, whilst impaction and interception predominate above 0.iv μm.[18] In betwixt, near the most penetrating particle size (MPPS) 0.21 μm, both diffusion and interception are comparatively inefficient.[xix] Because this is the weakest indicate in the filter'south operation, the HEPA specifications use the memory of particles almost this size (0.3 μm) to classify the filter.[18] However it is possible for particles smaller than the MPPS to not accept filtering efficiency greater than that of the MPPS. This is due to the fact that these particles can act as nucleation sites for generally condensation and form particles near the MPPS.[xix]
Gas filtration [edit]
HEPA filters are designed to arrest very fine particles finer, but they exercise non filter out gasses and odor molecules. Circumstances requiring filtration of volatile organic compounds, chemical vapors, or cigarette, pet or flatulence odors telephone call for the apply of an activated carbon (charcoal) or other type of filter instead of or in addition to a HEPA filter.[20] Carbon textile filters, claimed to be many times more efficient than the granular activated carbon form at adsorption of gaseous pollutants, are known as High Efficiency Gas Adsorption filters (HEGA) and were originally developed by the British Armed Forces as a defense against chemical warfare.[21] [22]
Pre-filter and HEPA filter [edit]
A HEPA purse filter can be used in conjunction with a pre-filter (usually carbon-activated) to extend the usage life of the more than expensive HEPA filter.[23] In such setup, the commencement phase in the filtration procedure is made upwardly of a pre-filter which removes most of the larger dust, hair, PM10 and pollen particles from the air. The second stage high-quality HEPA filter removes the effectively particles that escape from the pre-filter. This is common in air treatment units.
Specifications [edit]

A portable HEPA filtration unit used to clean air after a fire, or during manufacturing processes
Colour afterwards use of a HEPA filter in an extremely polluted city
HEPA filters, every bit divers past the United States Department of Energy (DOE) standard adopted by most American industries, remove at least 99.97% of aerosols 0.iii micrometers (μm) in diameter.[24] The filter'southward minimal resistance to airflow, or pressure drib, is commonly specified around 300 pascals (0.044 psi) at its nominal volumetric period rate.[7]
The specification used in the Eu: European Standard EN 1822-i:2009, from which ISO 29463 is derived,[4] defines several classes of filters by their retention at the given nearly penetrating particle size (MPPS): Efficient Particulate Air filters (EPA), HEPA and Ultra Depression Particulate Air filters (ULPA). The averaged efficiency of the filter is called "overall", and the efficiency at a specific point is called "local":[4]
| Efficiency | EN 1822 | ISO 29463 | Retention (averaged) | Retentivity (spot) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPA | E10 | — | ≥ 85% | — |
| E11 | ISO 15 E ISO 20 E | ≥ 95% ≥ 99% | — | |
| E12 | ISO 25 Eastward ISO 30 E | ≥ 99.five% ≥ 99.nine% | — | |
| HEPA | H13 | ISO 35 H ISO 40 H | ≥ 99.95% ≥ 99.99% | ≥ 99.75% ≥ 99.95% |
| H14 | ISO 45 H ISO 50 H | ≥ 99.995% ≥ 99.999% | ≥ 99.975% ≥ 99.995% | |
| ULPA | U15 | ISO 55 U ISO sixty U | ≥ 99.9995% ≥ 99.9999% | ≥ 99.9975% ≥ 99.9995% |
| U16 | ISO 65 U ISO seventy U | ≥ 99.99995% ≥ 99.99999% | ≥ 99.99975% ≥ 99.9999% | |
| U17 | ISO 75 U | ≥ 99.999995% | ≥ 99.9999% |
Meet also the different classes for air filters for comparison.
Today, a HEPA filter rating is applicable to whatever highly efficient air filter that tin attain the aforementioned filter efficiency performance standards as a minimum and is equivalent to the more than recent National Found for Occupational Condom and Health P100 rating for respirator filters. The United States Section of Free energy (DOE) has specific requirements for HEPA filters in DOE-regulated applications.
Marketing [edit]
Some companies utilize a marketing term known as "Truthful HEPA" to give consumers assurance that their air filters run into the HEPA standard, although this term has no legal or scientific meaning.[25] Products that are marketed to be "HEPA-type," "HEPA-like," "HEPA-style" or "99% HEPA" exercise not satisfy the HEPA standard and may not accept been tested in independent laboratories. Although such filters may come reasonably close to HEPA standards, others fall significantly short.[26]
Efficacy and rubber [edit]
In general terms (and allowing for some variation depending on factors such as the air-menstruation charge per unit, the concrete properties of the particles beingness filtered, as well as engineering details of the unabridged filtration-system design and not merely the filter-media properties), HEPA filters feel the well-nigh difficulty in capturing particles in the size range of 0.15 to 0.2 µm.[27] HEPA filtration works by mechanical ways, unlike ionic and ozone handling technologies, which use negative ions and ozone gas respectively. So, the likelihood of potential triggering of pulmonary side-furnishings such as asthma[28] and allergies is much lower with HEPA purifiers.[29]
To ensure that a HEPA filter is working efficiently, the filters should be inspected and changed at least every six months in commercial settings. In residential settings, and depending on the general ambient air quality, these filters tin be changed every two to three years. Failing to change a HEPA filter in a timely fashion volition consequence in it putting stress on the car or arrangement and not removing particles from the air properly. Additionally, depending on the gasketing materials called in the design of the organisation, a clogged HEPA filter tin can result in extensive bypassing of airflow around the filter.[30]
Applications [edit]

Biomedical [edit]
HEPA filters are critical in the prevention of the spread of airborne bacterial and viral organisms and, therefore, infection. Typically, medical utilize HEPA filtration systems also incorporate high-energy ultraviolet light units or panels with anti-microbial blanket to kill off the live bacteria and viruses trapped by the filter media.[ citation needed ] Some of the best-rated HEPA units take an efficiency rating of 99.995%, which assures a very high level of protection against airborne disease transmission.
COVID-19 [edit]
SARS‑CoV‑ii is approximately 0.125 µm. Airborne aerosol of SARS-CoV-2 could be captured by HEPA filters, even if they are on the floor.[ clarification needed ] [31] [32]
Vacuum cleaners [edit]

HEPA original filter for Philips FC87xx-series vacuum cleaners
Many vacuum cleaners besides utilize HEPA filters every bit role of their filtration systems. This is beneficial for asthma and allergy sufferers, because the HEPA filter traps the fine particles (such every bit pollen and house grit mite feces) which trigger allergy and asthma symptoms. For a HEPA filter in a vacuum cleaner to exist effective, the vacuum cleaner must be designed and so that all the air fatigued into the car is expelled through the filter, with none of the air leaking past it. This is ofttimes referred to as "Sealed HEPA" or sometimes the more vague "True HEPA". Vacuum cleaners simply labeled "HEPA" may take a HEPA filter, but not all air necessarily passes through information technology. Finally, vacuum cleaner filters marketed as "HEPA-like" will typically use a filter of a like construction to HEPA, just without the filtering efficiency. Considering of the actress density of a true HEPA filter, HEPA vacuum cleaners require more powerful motors to provide adequate cleaning power.
Some newer models claim to be better than the earlier ones with the inclusion of "washable" filters. Generally, washable true HEPA filters are expensive. A high-quality HEPA filter can trap 99.97% of dust particles that are 0.3 microns in bore. For comparison'due south sake, a human pilus is near 50 to 150 microns in diameter. So, a true HEPA filter is effectively trapping particles several hundred time smaller than the width of a human pilus.[33] Some manufacturers claim filter standards such as "HEPA 4," without explaining the significant behind them. This refers to their Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value (MERV) rating. These ratings are used to rate the power of an air cleaner filter to remove dust from the air as it passes through the filter. MERV is a standard used to measure the overall efficiency of a filter. The MERV scale ranges from ane to 16, and measures a filter's ability to remove particles from 10 to 0.three micrometer in size. Filters with college ratings not only remove more particles from the air, but they also remove smaller particles.
Heating, ventilation, and air workout [edit]
HEPA filter upshot within home HVAC system: without (OUTdoor) and with filter (INdoor)
Heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC)[34] is technology that uses air filters, such as HEPA filters, to remove pollutants from the air either indoors or in vehicles. Pollutants include smoke, viruses, powders, etc., and can originate either outside or inside. HVAC is used to provide ecology comfort and in polluted cities to maintain health.[ citation needed ]
Technical Specifications:[35]
| Filter Media | Microns Size | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| H10 | >0.v | 85% |
| H11 | >0.5 | 95% |
| H12 | >0.five | 99.v% |
| H13 | >0.three | 99.95% |
| H14 | >0.iii | 99.995% |
Vehicles [edit]
Airlines [edit]
Modernistic airliners use HEPA filters to reduce the spread of airborne pathogens in recirculated air. Critics accept expressed concern about the effectiveness and state of repair of air filtering systems, since they call back that much of the air in an airplane cabin is recirculated. Near all of the air in a pressurized aircraft is, in fact, brought in from the exterior, circulated through the cabin and then exhausted through outflow valves in the rear of the aircraft.[36] About forty percent of the cabin's air goes through a HEPA filter and the other 60 percent comes from exterior the plane. Certified air filters block and capture 99.97 pct of airborne particles.[37]
Motor vehicles [edit]
In 2016, it was announced that the Tesla Model X would accept the world's first HEPA-form filter in a Tesla machine.[38] Post-obit the release of the Model X, Tesla has updated the Model Due south to also have an optional HEPA air filter.[39] HEPA filters were used in many other vehicles before that.
History [edit]
| | This section needs expansion. You lot tin can help past adding to it. (December 2016) |
The idea behind the development of the HEPA filter was born from gas masks worn past soldiers fighting in World State of war II. A piece of paper establish inserted into a High german gas mask had a remarkably high capture efficiency for chemical fume. The British Ground forces Chemical Corps duplicated this and began to manufacture it in large quantities for their own service gas masks. They needed some other solution for operational headquarters, where individual gas masks were impractical. The Army Chemic Corps adult a combination mechanical blower and air purifier unit, which incorporated cellulose-asbestos paper in a deeply-pleated form with spacers between the pleats. Information technology was referred to as an "absolute" air filter and laid the groundwork for further research to come in developing the HEPA filter.[40]
The side by side phase of the HEPA filter was designed in the 1940s and was used in the Manhattan Projection to forestall the spread of airborne radioactive contaminants.[41] The U.s.a. Army Chemical Corps and National Defense Enquiry Committee needed to develop a filter suitable for removing radioactive materials from the air. The Army Chemical Corps asked Nobel Laureate Irving Langmuir to recommend filter test methods and other general recommendations for creating the cloth to filter out these radioactive particles. He identified 0.three micron size particles to exist the "most penetrating size"—the most difficult and concerning.[42]
It was commercialized in the 1950s, and the original term became a registered trademark and later a generic trademark for highly efficient filters.[14]
Over the decades filters have evolved to satisfy the higher and higher demands for air quality in various high technology industries, such as aerospace, pharmaceutical industry, hospitals, health care, nuclear fuels, nuclear ability, and integrated circuit fabrication.
Encounter likewise [edit]
- Air purifier – Device which removes contaminants from the air in a room
- Make clean air delivery rate – Filtration efficacy measurement
- Cleanroom – Room which is used for industrial or research processes that does not tolerate dust
- Electrostatic precipitator – trap particles with high voltage
- Hypoallergenic vacuum cleaner – vacuum cleaner with high efficiency air filter
- Minimum efficiency reporting value – Measurement scale for the effectiveness of air filters (MERV)
- Respirator – Device worn to protect the user from inhaling contaminants
- ULPA – Removes 99.999% of dust, pollen, mold, bacteria, and particles larger than 120 nm (0.12 μm)
- Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation – Disinfection method using ultraviolet light
References [edit]
Footnotes [edit]
- ^ "GLOSSARY". HEPA Corporation. Archived from the original on Apr 20, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ "HEPA". The Free Lexicon. Archived from the original on April 20, 2020. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ "Efficiency of the HEPA air filter: HEPA filter quality and bypassing". Air-Purifier-Power. Archived from the original on April xx, 2020. Retrieved May xiv, 2021.
- ^ a b c "INTERNATIONAL ISO STANDARD 29463-ane—High-efficiency filters and filter media for removing particles in air". International System for Standardization. October xv, 2011. Archived from the original on March eight, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ European Standard EN 1822-1:2009, "High efficiency air filters (EPA, HEPA and ULPA)", 2009
- ^ American Society of Mechanical Engineers, ASME AG-1a–2004, "Addenda to ASME AG-1–2003 Code on Nuclear Air and Gas Handling", 2004
- ^ a b Barnette, Sonya. "Specification for HEPA Filters Used by DOE Contractors — DOE Technical Standards Program". www.standards.doe.gov. Archived from the original on 2020-04-twenty. Retrieved 2019-06-05 .
- ^ Guidance for Filtration and Air-Cleaning Systems to Protect Edifice Environments from Airborne Chemical, Biological, or Radiological Attacks (PDF). Cincinnati, OH: National Establish for Occupational Condom and Health. Apr 2003. pp. 8–12. doi:10.26616/NIOSHPUB2003136. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 10, 2020. Retrieved February nine, 2020.
- ^ Godoy, Charlotte; Thomas, Dominique (2020-07-02). "Influence of relative humidity on HEPA filters during and after loading with soot particles". Droplets Science and Engineering science. 54 (seven): 790–801. Bibcode:2020AerST..54..790G. doi:x.1080/02786826.2020.1726278. ISSN 0278-6826. S2CID 214275203. Archived from the original on 2021-05-16. Retrieved 2021-03-04 .
- ^ Payet, S.; Boulaud, D.; Madelaine, G.; Renoux, A. (1992-x-01). "Penetration and pressure drib of a HEPA filter during loading with submicron liquid particles". Journal of Aerosol Science. 23 (seven): 723–735. Bibcode:1992JAerS..23..723P. doi:10.1016/0021-8502(92)90039-X. ISSN 0021-8502. Archived from the original on 2021-05-16. Retrieved 2021-03-05 .
- ^ Schentag, Jerome J.; Akers, Charles; Campagna, Pamela; Chirayath, Paul (2004). SARS: CLEARING THE AIR. National Academies Press (U.s.a.). Archived from the original on 2021-01-05. Retrieved 2021-03-04 .
- ^ Chuaybamroong, P.; Chotigawin, R.; Supothina, S.; Sribenjalux, P.; Larpkiattaworn, South.; Wu, C.-Y. (2010). "Efficacy of photocatalytic HEPA filter on microorganism removal". Indoor Air. 20 (three): 246–254. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0668.2010.00651.ten. ISSN 1600-0668. PMID 20573124.
- ^ Guo, Jianguo; Xiong, Yi; Kang, Taisheng; Xiang, Zhiguang; Qin, Chuan (2020-04-fourteen). "Bacterial community analysis of flooring grit and HEPA filters in air purifiers used in role rooms in ILAS, Beijing". Scientific Reports. ten (ane): 6417. Bibcode:2020NatSR..10.6417G. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-63543-1. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC7156680. PMID 32286482.
- ^ a b Gantz, Carroll (2012-09-21). The Vacuum Cleaner: A History. McFarland. p. 128. ISBN9780786493210. Archived from the original on 2021-05-16. Retrieved 2020-11-11 .
- ^ "Nearly HEPA". hepa.com. Archived from the original on 2020-04-twenty. Retrieved 2019-06-05 .
- ^ Gupta, Shakti Kumar; Kant, Sunil (Dec i, 2007). Modern Trends in Planning and Designing of Hospitals: Principles and Practice. Jaypee Brothers. p. 199. ISBN978-8180619120. OCLC 1027907136.
- ^ Christopherson, David A.; Yao, William C.; Lu, Mingming; Vijayakumar, R.; Sedaghat, Ahmad R. (July 14, 2020). "High-Efficiency Particulate Air Filters in the Era of COVID-19: Function and Efficacy". Otolaryngology–Caput and Cervix Surgery. 163 (6): 1153–1155. doi:10.1177/0194599820941838. PMID 32662746. S2CID 220518635. Archived from the original on November 3, 2020. Retrieved May fifteen, 2021 – via SAGE journals.
- ^ a b Woodford, Chris (May 21, 2008). "How exercise HEPA air filters work?". Explicate That Stuff. Archived from the original on April 20, 2020. Retrieved May 15, 2021.
- ^ a b da Roza, R. A. (December 1, 1982). "Particle size for greatest penetration of HEPA filters—and their true efficiency". U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Data. doi:10.2172/6241348. OSTI 6241348. Archived from the original on May sixteen, 2021. Retrieved May 15, 2021.
- ^ Khan, Faisal I; Ghoshal, Aloke Kr. (November 2000). "Removal of Volatile Organic Compounds from polluted air" (PDF). Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries. Elsevier. 13 (6): 527–545. doi:10.1016/S0950-4230(00)00007-3. ISSN 0950-4230. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 15, 2017. Retrieved May fifteen, 2021.
- ^ Glover, Norman J. (May 2002). "Countering chemical and biological terrorism". Civil Technology. New York Metropolis: American Society of Civil Engineers. 72 (5): 62–67. ISSN 0885-7024. OCLC 926218714. ProQuest 228557557.
- ^ Jonathan (August 19, 2016). "Air Purifier Acronyms - Stripping Out The Tech Jargon". Air Enhancing. Archived from the original on Apr 20, 2020. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ "Air Purifier Pre-Filter Replacement: The Prefilter Experiments". Air-Purifier-Ability. Archived from the original on April 20, 2020. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ Perryman, Oliver (December 3, 2020). "Do HEPA filters or air purifiers remove carbon monoxide?". Dehumidifier Critic. Archived from the original on May 16, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ Bretag, Scott (March 18, 2020). "Air Conditioners, HEPA Filters, And Airborne Allergens". Pulse Electric. Archived from the original on March 10, 2021. Retrieved May xvi, 2021.
- ^ "HEPA-Type Filter: The Nifty Pretender". Air-Purifier-Power. Archived from the original on February 25, 2021. Retrieved May sixteen, 2021.
- ^ Christopherson, David A.; Yao, William C.; Lu, Mingming; Vijayakumar, R.; Sedaghat, Ahmad R. (2020-07-14). "High-Efficiency Particulate Air Filters in the Era of COVID-19: Role and Efficacy". Otolaryngology–Caput and Cervix Surgery. 163 (6): 1153–1155. doi:ten.1177/0194599820941838. ISSN 0194-5998. PMID 32662746. S2CID 220518635. Archived from the original on 2021-05-16. Retrieved 2021-05-16 .
- ^ Dunkin, Mary Anne (April 30, 2010). "HEPA Filter Benefits for Allergy Relief". WebMD. Reviewed by Nayana Ambardekar. Archived from the original on March 29, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ "How do HEPA Filters Aid in Cleaning Indoor Air - Consummate Guide". Pure Air Hu. Archived from the original on October 20, 2019. Retrieved May sixteen, 2021.
- ^ Kelly, Tammy (March 14, 2018). "How Often Should A HEPA Filter Be Changed". Janitized. Archived from the original on March 8, 2021. Retrieved May sixteen, 2021.
- ^ Elias, Blake; Bar-Yam, Yaneer (March 9, 2020). "Could Air Filtration Reduce COVID-19 Severity and Spread?". New England Complex Systems Establish. Archived from the original on March 21, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ Heffernan, Tim (November 18, 2020). "Can HEPA Air Purifiers Capture the Coronavirus?". Wirecutter. Archived from the original on May 11, 2021. Retrieved May xvi, 2021.
- ^ Anand, Mohit (November 23, 2020). "Understanding the Home Air Purifier Engineering in Use Today". Honeywell Connection. Archived from the original on May 16, 2021. Retrieved May sixteen, 2021.
- ^ Hvac. Merriam-Webster. Archived from the original on Jan 15, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ "HVAC Air Filter Media Manufacturers in Bharat | ULPA Air Filter Media at Best Toll". PARK Non Woven . Retrieved 2021-xi-27 .
- ^ Smith, Patrick (July 22, 2012). "The truth about cabin air". AskThePilot.com. Archived from the original on May half-dozen, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ Read, Johanna (August 28, 2020). "How clean is the air on planes?". National Geographic. National Geographic Partners. Archived from the original on May half dozen, 2021. Retrieved May xvi, 2021.
- ^ "Putting the Tesla HEPA Filter and Bioweapon Defense Mode to the Test". Tesla, Inc. May 2, 2016. Archived from the original on April 27, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ Voelcker, John (April 12, 2016). "2016 Tesla Model Due south gets styling update, 48-amp charger, new interior options, $i,500 price increase (updated)". Dark-green Car Reports. Archived from the original on February 24, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ Commencement, Melvin Westward. (March 1, 1998). "HEPA Filters". Journal of the American Biological Safe Association. American Biological Prophylactic Association. iii (ane): 33–42. doi:10.1177/109135059800300111. ISSN 1091-3505. S2CID 207941359. Archived from the original on May 16, 2021. Retrieved May 16, 2021.
- ^ Ogunseitan, Oladele; Robbins, Paul, eds. (2011). Green Health: An A-to-Z Guide. Los Angeles: SAGE Publishing. p. xiii. ISBN9781412996884. OCLC 793012578. Archived from the original on 2021-05-17. Retrieved 2016-12-eighteen .
- ^ "The History of HEPA Filters". APC Filters. November 21, 2019. Archived from the original on March 26, 2021. Retrieved May xvi, 2021.
Further reading [edit]
- TSI Application Note ITI-041: Mechanisms of Filtration for High Efficiency Fibrous Filters
External links [edit]
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HEPA
Posted by: terrellhorer1946.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Clean Hepa Filter Shark Xhf680"
Post a Comment